-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
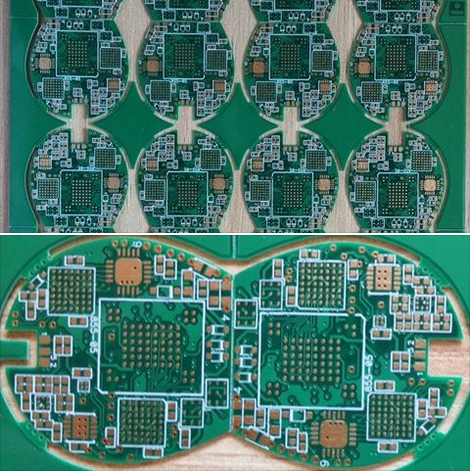
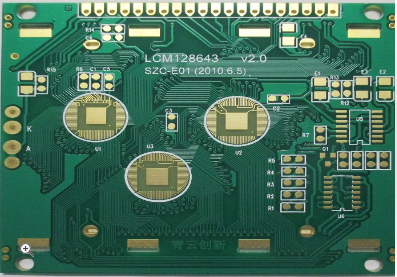
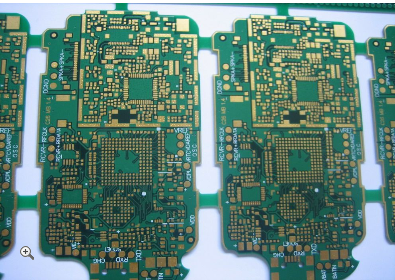
Advanced Plating Half Holes PCB Technology For Enhanced Electrical Connectivity And Reliability In Modern Electronics
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern electronics, where devices are becoming increasingly compact, powerful, and interconnected, the demand for printed circuit boards (PCBs) that offer superior electrical connectivity and unwavering reliability has never been greater. Traditional PCB manufacturing techniques, while foundational, often encounter limitations when dealing with high-density interconnects, miniaturized components, and the rigorous performance standards of applications like 5G infrastructure, advanced automotive systems, and sophisticated medical devices. This is where Advanced Plating Half Holes PCB Technology emerges as a pivotal innovation. This sophisticated process involves creating plated half-holes, or castellated holes, along the edges of a PCB, which serve as both mounting points and conductive pathways. By seamlessly integrating these plated half-holes, this technology fundamentally enhances the board's ability to form robust, low-resistance connections in complex multi-board assemblies or module-to-carrier board interfaces, directly addressing the critical needs for signal integrity, power delivery, and mechanical stability in today's cutting-edge electronic designs.
The Technical Mechanics and Manufacturing Precision of Half-Hole Plating
The creation of advanced plated half-holes is a testament to precision engineering. The process begins with a standard PCB panel where holes are drilled precisely along the intended board edge. A critical step follows: the panel is routed or scored, effectively slicing these holes in half and creating the characteristic castellated profile. The true technological advancement lies in the subsequent plating phase. A meticulous metallization process is applied, which typically involves electrodes copper plating followed by a final finish, such as Immersion Silver, ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), or hard gold.
This plating must be uniform and continuous, covering the entire semicircular surface of the hole, from the outer rim, down the curved barrel, and onto the inner pad. Achieving this consistent, void-free metallic layer is paramount. Any imperfection can become a point of high resistance or eventual failure. Modern manufacturing employs advanced chemical processes and controlled automation to ensure the plating thickness and adhesion meet stringent specifications, creating a perfectly formed, reliable conductive half-cylinder that is integral to the board substrate itself.
Revolutionizing Electrical Connectivity and Signal Integrity
The primary advantage of this technology is its transformative impact on electrical connectivity. Plated half-holes provide a direct, soldered connection between two boards, effectively creating a continuous conductive path that minimizes parasitic inductance and capacitance compared to traditional connectors or headers. This direct connection is crucial for high-frequency applications, such as RF (Radio Frequency) modules, antenna boards, and high-speed digital interfaces, where signal loss and reflection must be minimized.
Furthermore, the robust metallic structure offers excellent current-carrying capacity. The plated surface area of the half-hole is significantly larger than that of a simple surface pad, allowing for better heat dissipation and reduced current density at the joint. This results in lower operational temperatures and enhanced long-term reliability for power lines. The result is a system with improved signal integrity, reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI), and more efficient power distribution, all of which are non-negotiable in modern high-performance electronics.
Enhancing Mechanical Reliability and Assembly Efficiency
Beyond electrical performance, advanced plated half-holes confer exceptional mechanical benefits. When soldered to a corresponding carrier board, the half-hole forms a strong, durable mechanical bond. The solder fillet that forms around the plated semicircle provides substantial shear strength, making the assembly highly resistant to vibration, mechanical shock, and thermal cycling stresses—common challenges in automotive, aerospace, and industrial environments.
This design also streamlines the assembly process. It enables a compact, space-saving board-to-board stacking or edge-mounting configuration, eliminating the need for bulky connectors and saving valuable real estate within the device. The assembly can often be accomplished using standard reflow soldering techniques, facilitating automated, high-volume production. This combination of mechanical robustness and assembly-friendly design reduces overall system size, weight, and potential points of failure, while simultaneously lowering manufacturing complexity and cost.
Critical Applications Driving Adoption Across Industries
The unique benefits of this technology have made it indispensable in several advanced sectors. In telecommunications, particularly for 5G small cells and network infrastructure equipment, plated half-hole PCBs are used to mount RF power amplifiers and filter modules, ensuring impeccable signal integrity in a compact form factor. The automotive industry, especially in electric and autonomous vehicles, relies on them for robust connections in battery management systems (BMS), advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) controllers, and dense infotainment units.
Similarly, in medical electronics, where reliability is paramount, the technology is used in miniaturized implantable devices, diagnostic sensors, and portable monitors. Internet of Things (IoT) gateways and wearable technology also leverage these PCBs to achieve reliable interconnections in extremely miniaturized packages. In each case, the technology solves the dual challenge of maintaining peak electrical performance while ensuring the physical durability required by the application's operating environment.
Future Trajectory and Evolving Design Considerations
As electronic devices continue their trend toward further miniaturization and increased functional integration, the role of advanced plated half-hole technology is set to expand. Future developments will likely focus on refining plating chemistries for even better uniformity and compatibility with lead-free, high-temperature solders. Integration with other advanced PCB technologies, such as embedded components and high-density interconnect (HDI) layouts, will create even more sophisticated and compact system-in-package solutions.
For designers, adopting this technology requires careful forethought. Considerations include optimal half-hole diameter and pitch for the target soldering process, appropriate plating finish selection based on shelf-life and soldering requirements, and precise panelization design to facilitate clean breakout after routing. Collaboration with a PCB manufacturer possessing proven expertise in this precise process is crucial to navigate these parameters and fully harness the technology's potential for enhanced connectivity and reliability, paving the way for the next generation of electronic innovation.
REPORT