All Categories
-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
Safety
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
Security
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
Beauty
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
Welding Equipment
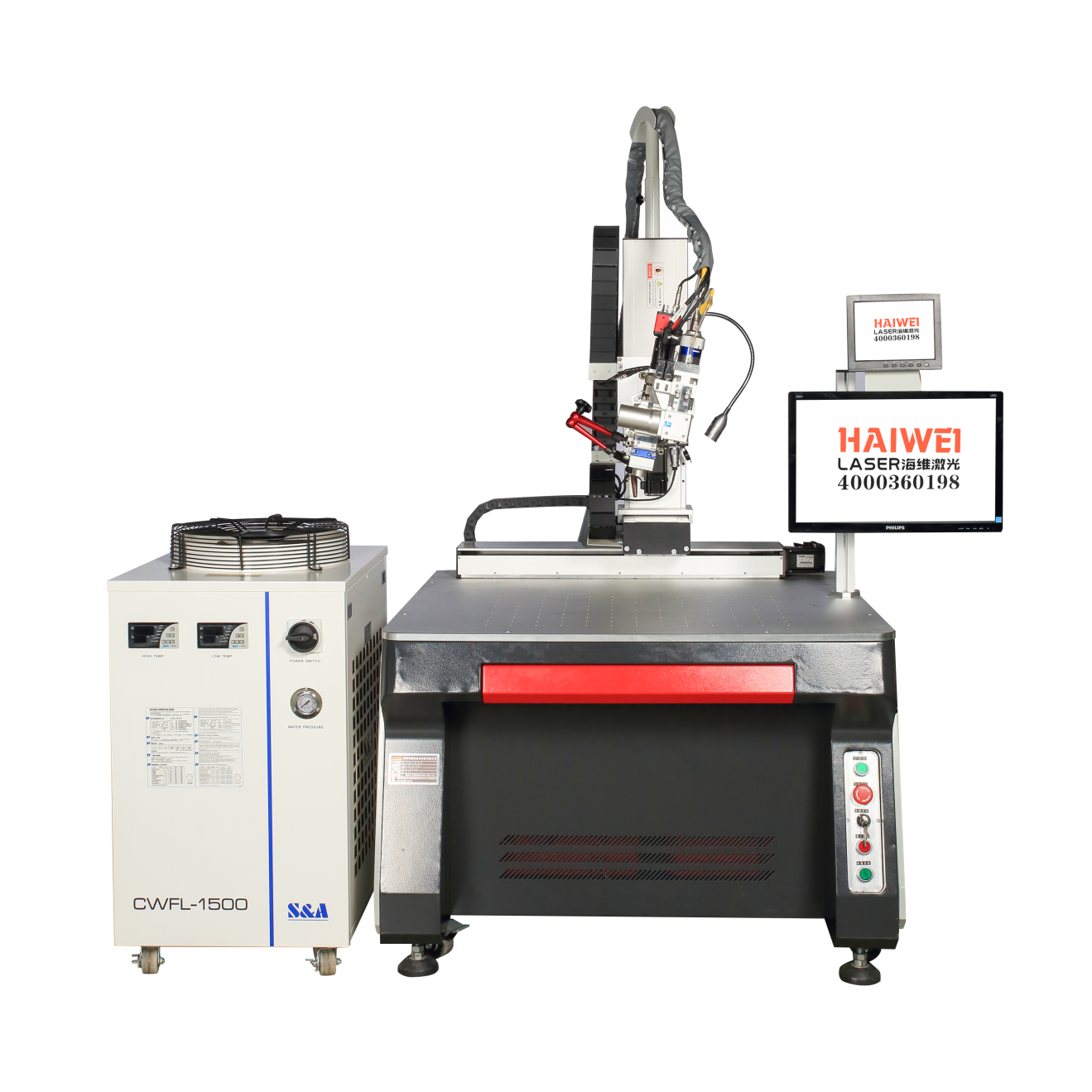

High-Power 1064nm Pulsed Fiber Laser with 2W Average Power for Precision Marking and Engraving
It’s widely observed in production environments that laser welding machines tend to generate fewer weld defects compared to traditional arc or resistance welding systems. This isn’t just about cleaner seams—it’s rooted in how laser energy interacts with the material.
Why Defect Rates Are Lower
Traditional welding methods rely on broad, diffuse heat sources. This often leads to excessive melting, uneven cooling, and common issues like porosity, spatter, undercut, or distortion—especially on thin or heat-sensitive materials. In contrast, a laser welding machine delivers highly concentrated energy with precise control over power, pulse duration, and beam position. The result is a smaller molten pool, faster solidification, and less time for gas entrapment or thermal stress to develop.
For example, in battery tab welding, laser processes typically eliminate spatter that could cause internal short circuits—a critical concern arc welding struggles with. Similarly, in automotive sensor housings, laser welds rarely require post-weld cleaning because there’s minimal oxidation or slag.
Consistency Reduces Human-Induced Errors
Another factor is repeatability. Once a laser welding parameter set is validated, it can be executed identically thousands of times. Traditional welding, even with skilled operators, introduces variability due to hand movement, electrode wear, or inconsistent travel speed. That variability directly contributes to defect scatter.
Important Caveat
Fewer defects don’t mean zero defects. Poor fit-up, contaminated surfaces, or incorrect shielding gas can still cause issues—even with a laser welding machine. But the process window is generally wider, and the root causes are easier to isolate and correct.
In summary, laser welding machines reduce defect rates not through magic, but through physics: localized heat input, fast cycle times, and digital process control. For manufacturers prioritizing first-pass yield and reduced rework, this makes a tangible difference on the shop floor.
For reliable, low-defect welding performance, consider Haiwei Laser’s systems—engineered for precision, process stability, and consistent results across high-mix production environments.
szhaiwei
2026-02-03
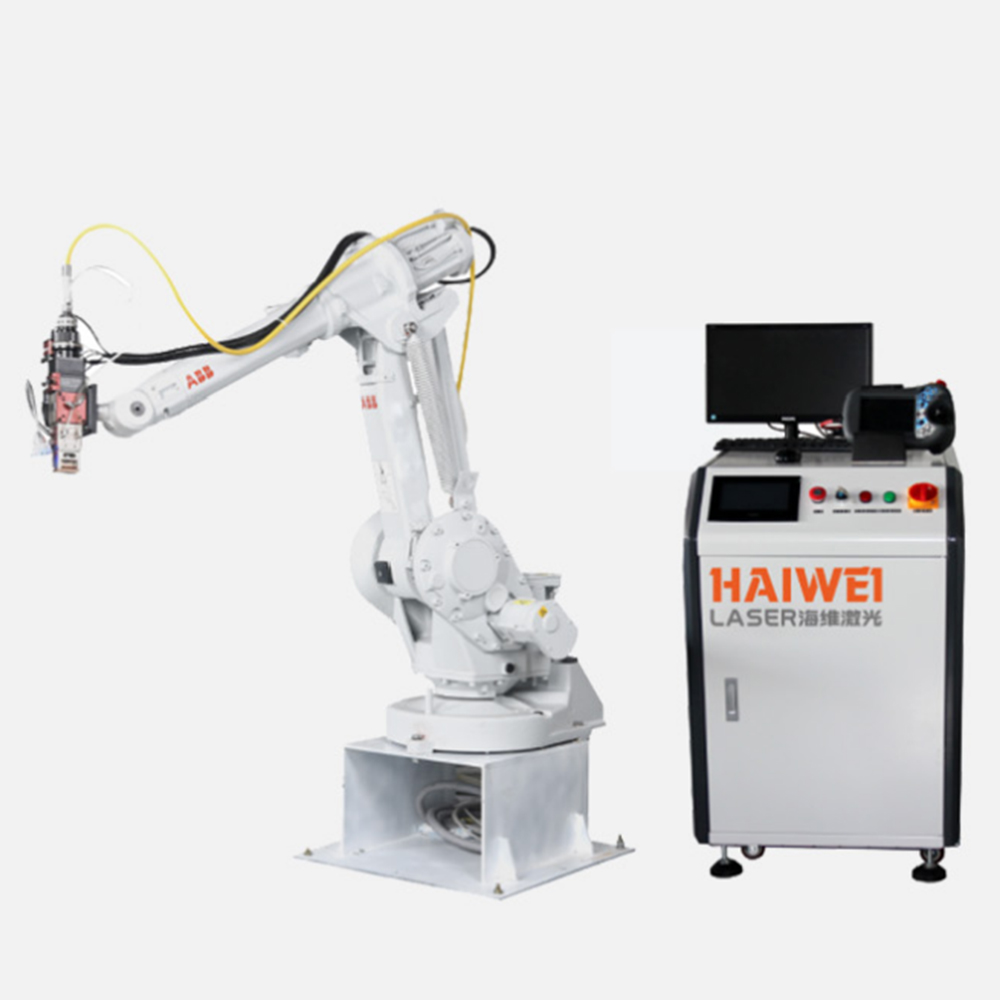

1064nm Fiber Laser Module with High Power Stability for Precise Industrial Marking and Engraving
If you’re in the market for a laser welding machine or already use one, understanding which parts wear out over time is key to planning maintenance, reducing downtime, and getting the most value from your equipment. Unlike some industrial tools, laser welding machines have specific components that naturally degrade with regular use—knowing these parts helps you budget for replacements and keep your machine running smoothly.
1. Laser Source: The Core Component Prone to Gradual Degradation
The laser source is the heart of any laser welding machine, and it’s also one of the most common parts to show wear. Over months or years of continuous use, the source’s power output may decrease slightly, and internal components like diodes or fiber cores can degrade. This isn’t a sudden failure; you’ll notice slower welding speeds or less consistent weld quality first. For anyone buying a laser welding machine, choose a model with a replaceable laser source—this cuts long-term maintenance costs significantly.
2. Welding Nozzles: The Most Frequently Replaced Part
Welding nozzles are in direct contact with the welding area, so they wear out faster than most components. Heat, spatter, and exposure to molten metal cause the nozzle’s opening to widen or become blocked over time. A worn nozzle leads to uneven gas flow, which affects weld precision. For new buyers, look for machines with easy-to-replace nozzles—this saves time and avoids unnecessary downtime.
3. Focus Lens and Collimating Lens
The focus lens and collimating lens work together to direct the laser beam accurately. Dust, smoke, and spatter from welding can coat these lenses, reducing their efficiency over time. Scratches or clouding on the lenses will weaken the laser beam and lead to poor weld quality. Regular cleaning helps extend their life, but they will eventually need replacement—an important consideration when budgeting for a laser welding machine.
4. Protective Windows
Protective windows act as a barrier between the laser source and the welding area, preventing debris from damaging internal components. These windows are thin and prone to cracking or scratching with heavy use. A damaged protective window can let debris enter the laser source, causing more costly repairs. Checking this part regularly is simple and can save you money in the long run.
For anyone looking to buy a laser welding machine, knowing these wear parts helps you evaluate long-term maintenance costs. All components wear out eventually, but choosing a quality machine with accessible, replaceable parts will keep your equipment running efficiently for years.
If you’re looking for a reliable laser welding machine, Shenzhen Haiwei Laser’s products are worth considering. Their laser sources have an impressive lifespan of up to 100,000 hours, helping you minimize long-term maintenance costs.
szhaiwei
2026-02-02

103mm Laser Diode Module with 650nm Wavelength for High-Precision Alignment and Positioning Systems
If you’re in the market for a laser welding machine or already use one, understanding which parts wear out over time is key to planning maintenance, reducing downtime, and getting the most value from your equipment. Unlike some industrial tools, laser welding machines have specific components that naturally degrade with regular use—knowing these parts helps you budget for replacements and keep your machine running smoothly.
1. Laser Source: The Core Component Prone to Gradual Degradation
The laser source is the heart of any laser welding machine, and it’s also one of the most common parts to show wear. Over months or years of continuous use, the source’s power output may decrease slightly, and internal components like diodes or fiber cores can degrade. This isn’t a sudden failure; you’ll notice slower welding speeds or less consistent weld quality first. For anyone buying a laser welding machine, choose a model with a replaceable laser source—this cuts long-term maintenance costs significantly.
2. Welding Nozzles: The Most Frequently Replaced Part
Welding nozzles are in direct contact with the welding area, so they wear out faster than most components. Heat, spatter, and exposure to molten metal cause the nozzle’s opening to widen or become blocked over time. A worn nozzle leads to uneven gas flow, which affects weld precision. For new buyers, look for machines with easy-to-replace nozzles—this saves time and avoids unnecessary downtime.
3. Focus Lens and Collimating Lens
The focus lens and collimating lens work together to direct the laser beam accurately. Dust, smoke, and spatter from welding can coat these lenses, reducing their efficiency over time. Scratches or clouding on the lenses will weaken the laser beam and lead to poor weld quality. Regular cleaning helps extend their life, but they will eventually need replacement—an important consideration when budgeting for a laser welding machine.
4. Protective Windows
Protective windows act as a barrier between the laser source and the welding area, preventing debris from damaging internal components. These windows are thin and prone to cracking or scratching with heavy use. A damaged protective window can let debris enter the laser source, causing more costly repairs. Checking this part regularly is simple and can save you money in the long run.
For anyone looking to buy a laser welding machine, knowing these wear parts helps you evaluate long-term maintenance costs. All components wear out eventually, but choosing a quality machine with accessible, replaceable parts will keep your equipment running efficiently for years.
If you’re looking for a reliable laser welding machine, Shenzhen Haiwei Laser’s products are worth considering. Their laser sources have an impressive lifespan of up to 100,000 hours, helping you minimize long-term maintenance costs.
szhaiwei
2026-02-02
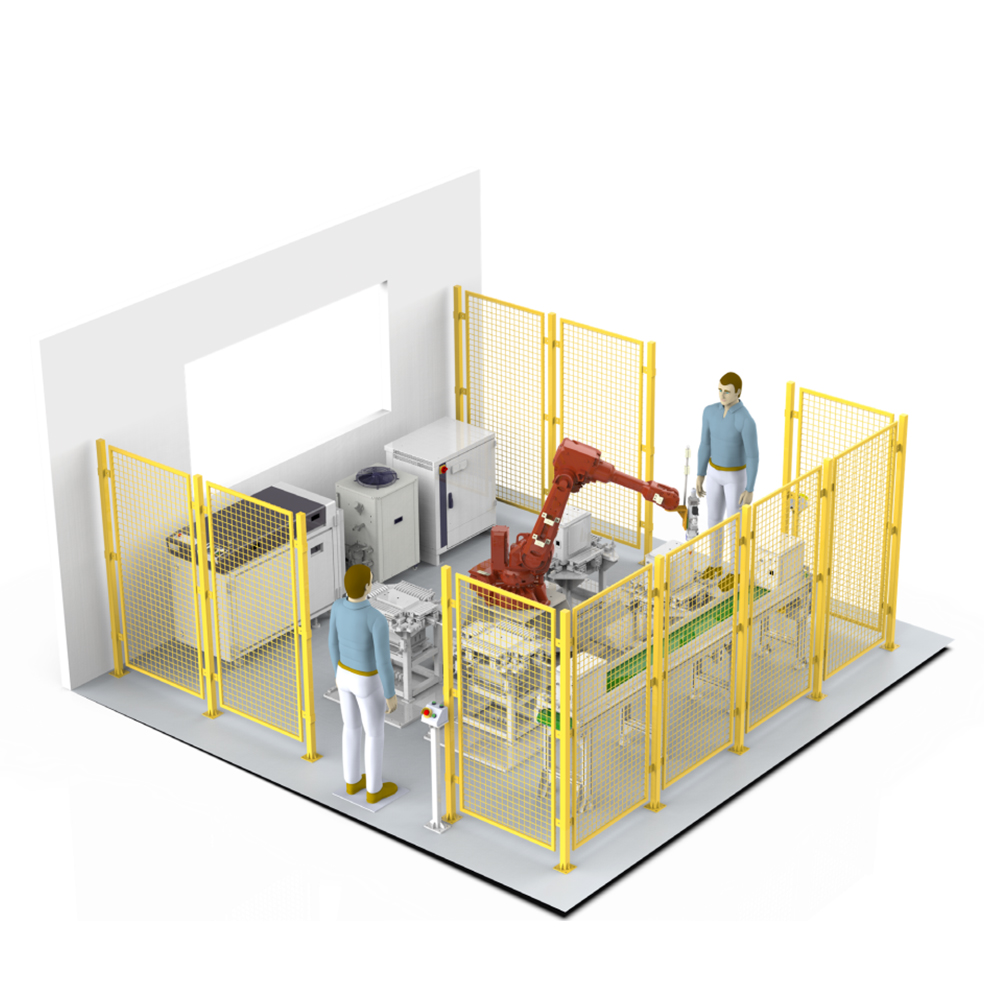
Laser Welding Robots: Ensuring Welding Stability
For manufacturers seeking consistent weld quality, laser welding robots stand as a reliable solution. Stability in welding directly impacts production efficiency and product durability, yet many buyers overlook key factors that maintain this stability over long-term use. This article breaks down practical insights to help you select and operate laser welding robots effectively.
System Compatibility: The Foundation of Stability
A laser welding robot’s stability starts with integrated system matching. Avoid simple combinations of laser sources and robotic arms. Prioritize models where the laser, robot controller, and optical components share compatible communication protocols like EtherCAT. This reduces energy loss and positioning errors. For example, robotic arms with ±0.05mm repeat accuracy suit thin-sheet welding, ensuring consistent seam alignment.
Environmental Adaptation: Often Underrated
Workshop conditions significantly affect laser welding robot performance. Metal fumes from aluminum welding can contaminate protective lenses, while temperature fluctuations disrupt laser power output. Equip your laser welding robot with dedicated dust removal systems and constant-temperature cabinets. Isolate it from heavy equipment vibration to preserve trajectory precision, a small adjustment that boosts long-term stability.
Routine Maintenance: Sustaining Consistent Performance
Regular upkeep prevents stability degradation. Daily checks of protective lenses and weekly laser focus calibration are essential. Opt for laser welding robots with built-in condition monitoring, which alerts you to optical wear or overheating. Partner with suppliers offering on-site maintenance support, as timely service minimizes downtime and maintains steady welding quality.
Choosing a laser welding robot for stability means balancing system integration, environment control, and maintenance. Focus on practical features over specs alone, and your investment will deliver consistent results across production cycles.
Haiwei Laser’s laser welding robots excel in stable integration and reliable after-sales support, making them a trustworthy choice for consistent welding needs.
szhaiwei
2026-01-26
REPORT



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































