-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
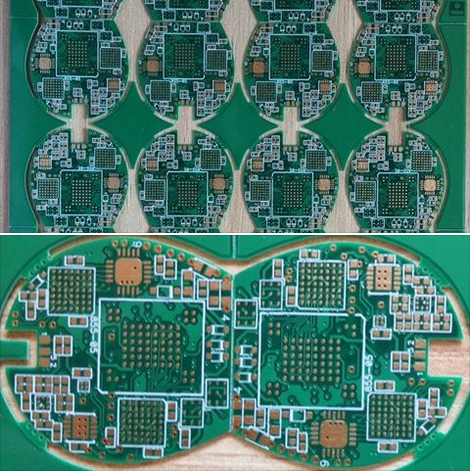
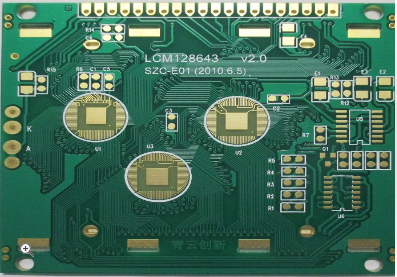
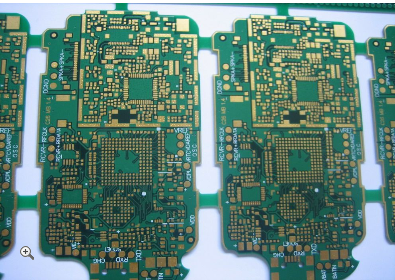
Reliable HDI Printed Circuit Board Production Ensuring High Yield And Quality For Demanding Industrial And Medical Equipment
In the rapidly advancing landscape of modern technology, the demand for more compact, powerful, and reliable electronic systems has never been greater, particularly within the industrial and medical sectors. At the heart of these sophisticated systems lies a critical component: the High-Density Interconnect (HDI) printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike conventional PCBs, HDI boards incorporate finer lines, microvias, and higher connection pad density, enabling enhanced performance in a reduced footprint. For applications such as industrial automation controllers, diagnostic imaging equipment, patient monitoring devices, and surgical robots, failure is not an option. These environments demand unwavering reliability, exceptional signal integrity, and resilience under harsh conditions. Therefore, the production of reliable HDI PCBs—ensuring both high manufacturing yield and impeccable quality—is not merely a manufacturing goal but a fundamental necessity. It bridges the gap between ambitious electronic design and real-world, mission-critical application, making it a pivotal topic for engineers, procurement specialists, and industry stakeholders who seek to understand how cutting-edge electronics can meet the stringent demands of today's most challenging fields.
The Imperative of Advanced Materials and Laminates
The foundation of any reliable HDI PCB is the material from which it is constructed. For industrial and medical applications, standard FR-4 laminates often fall short. These demanding fields require substrates with superior thermal performance, dimensional stability, and consistent dielectric properties. High-performance materials like polyimide, Rogers, or specialized halogen-free FR-4 are frequently employed. These advanced laminates can withstand the higher temperatures associated with lead-free soldering processes and provide the necessary thermal management for densely packed components.
Furthermore, material selection directly impacts signal integrity, a non-negotiable aspect for high-speed digital circuits in diagnostic machines or sensitive analog signals in monitoring equipment. The dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df) of the laminate must be tightly controlled across the entire board and batch-to-batch to prevent signal loss, distortion, or crosstalk. The use of low-loss materials ensures that high-frequency signals, crucial in medical imaging or high-speed data acquisition in industrial settings, are transmitted with fidelity. Thus, a reliable HDI production process begins with rigorous material qualification and supply chain control, ensuring every layer of the board contributes to its ultimate performance and longevity.
Precision in Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Layout
Before the first layer is etched, the reliability of an HDI PCB is largely determined by its design. This phase, known as Design for Manufacturability (DFM), is a collaborative process between the design engineer and the PCB fabricator. For HDI boards, DFM rules are exceptionally stringent. It involves optimizing the layout to accommodate microvias—laser-drilled holes with diameters often less than 150 microns—and staggered or stacked via structures that connect multiple layers. A design that ignores fabrication capabilities can lead to drill breakage, poor plating, or unreliable interconnections, catastrophically lowering yield.
The layout must also account for controlled impedance, which is vital for maintaining signal integrity. This requires precise calculation and control of trace width, spacing, and proximity to reference planes. In medical devices, where patient safety is paramount, and in industrial equipment subject to electromagnetic interference (EMI), proper grounding schemes and shielding within the PCB layout are essential. By integrating DFM checks early, potential failure points are eliminated, manufacturing processes are streamlined, and the foundation for a high-yield, high-quality production run is firmly established. This proactive approach prevents costly redesigns and delays, ensuring the final product performs as intended in its demanding operational environment.
The Critical Role of State-of-the-Art Fabrication Processes
The actual fabrication of HDI PCBs is a symphony of advanced and meticulously controlled processes. Laser drilling for microvias is a cornerstone technology, offering precision unattainable with mechanical drilling. The consistency of the laser's focus, energy, and pulse duration must be perfectly calibrated to create clean, uniform vias in various materials without causing thermal damage to the surrounding substrate. Following drilling, the plating process is equally critical. Copper electroplating must achieve a uniform, void-free deposition within these microscopic holes to establish a robust electrical connection. Any thin spot or void can become a point of high resistance or an open circuit under thermal stress.
Another pivotal step is the lamination of multiple, often very thin, core layers. The process requires exact control of pressure, temperature, and vacuum to eliminate air pockets (delamination) and ensure perfect registration between layers. Misalignment can render a complex multilayer board useless. Finally, the solder mask application and surface finish (such as Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold or Immersion Silver) must provide a flat, reliable surface for component assembly while protecting the fine copper traces from oxidation and environmental corrosion. Each of these processes is supported by automated optical inspection (AOI) and electrical testing at multiple stages, creating a closed-loop system that identifies and corrects defects in real time, thereby safeguarding yield and quality.
Rigorous Testing, Inspection, and Quality Assurance Protocols
Producing a reliable HDI PCB does not end with fabrication; it is validated through an exhaustive regime of testing and inspection. This is the final gatekeeper before boards are shipped for assembly. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems scan every layer for defects like shorts, opens, or insufficient solder mask coverage. For the internal layers of an HDI board, which are invisible after lamination, this step is indispensable. Following AOI, electrical testing is performed using flying probe or dedicated fixture testers to verify netlist connectivity and ensure there are no open or short circuits.
For the most demanding applications, additional tests are mandatory. Controlled impedance testing confirms that high-speed signal traces meet their specified impedance values. Thermal stress testing, such as Thermal Cycle Testing (TCT) or Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT), subjects samples to extreme temperature fluctuations to simulate years of operation and identify potential weaknesses in materials or plated through-holes. In the medical field, compliance with standards like ISO 13485 for quality management systems is not optional. A reliable manufacturer will embed these quality assurance protocols into every stage of production, creating a comprehensive traceability record for each batch. This diligence ensures that every HDI PCB delivered will perform reliably in the field, upholding the safety and efficacy of medical devices and the continuous operation of industrial machinery.
The Impact on End-Application Performance and Lifecycle
The culmination of advanced materials, precise design, sophisticated fabrication, and rigorous testing is an HDI PCB that excels in its end application. In an MRI machine, this translates to clearer images without noise introduced by the electronics. In a portable ventilator, it means unwavering operation in diverse environmental conditions. For an industrial robot on a factory floor, it ensures millions of cycles of precise movement without electronic failure. The high yield in production also has a direct business impact, reducing unit cost and preventing shortages of critical components for equipment manufacturers.
Ultimately, the reliability engineered into these boards extends the operational lifecycle of the entire system, reducing downtime, maintenance costs, and the risk of catastrophic failure. In sectors where equipment availability can mean the difference between life and death or between profit and massive operational loss, this reliability is the ultimate return on investment. By mastering the art and science of reliable HDI PCB production, manufacturers empower innovators to push the boundaries of what is possible in industrial automation and medical technology, creating a safer, more efficient, and more connected world.
REPORT