-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
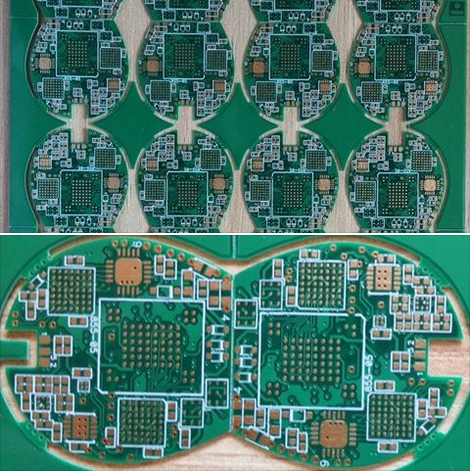
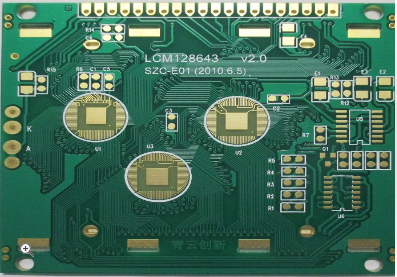
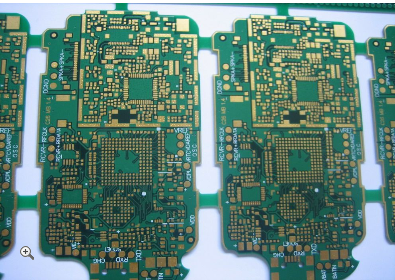
Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering Delivering Precision And Quality For Advanced Circuit Designs
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics, where miniaturization and high-density interconnections are paramount, the demand for advanced printed circuit board (PCB) technologies has never been greater. Among these, Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering stands out as a critical enabler for sophisticated circuit designs, delivering unparalleled precision and quality. This specialized process, often referred to as castellated holes or plated half-holes, involves creating plated semi-circular holes along the edges of a PCB. These features are essential for creating reliable board-to-board connections, module stacking, or edge connectors in compact devices such as IoT modules, wireless communication systems, and advanced medical equipment. As electronic devices become more complex and space-constrained, the engineering behind plating half holes ensures robust electrical performance and mechanical stability, making it a cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing. By focusing on meticulous design, material selection, and plating techniques, this technology addresses the challenges of high-frequency signals, thermal management, and durability, thereby captivating engineers and designers who seek to push the boundaries of innovation.
The Engineering Principles Behind Plating Half Holes
At its core, Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering revolves around creating precise, metallized semi-circular cutouts on the board edges. This process begins with careful design, where engineers specify the diameter, spacing, and plating thickness of the half holes using advanced CAD software. The holes are typically drilled or routed as full holes during the initial PCB fabrication stage, after which the board is milled along its edge to bisect these holes, leaving a plated half-circle. The plating itself involves multiple layers, starting with electroless copper deposition to establish a conductive base, followed by electrolytic copper plating to build up thickness, and often finishing with a surface finish such as ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) to enhance solderability and corrosion resistance.
The complexity of this engineering lies in maintaining consistency and integrity throughout the process. Factors like drill alignment, milling accuracy, and plating uniformity must be tightly controlled to prevent defects such as incomplete plating, cracks, or uneven surfaces. Advanced manufacturers employ automated optical inspection (AOI) and cross-sectional analysis to verify that each half hole meets stringent tolerances, often within microns. This attention to detail ensures that the plated half holes provide reliable electrical pathways and strong mechanical bonds when soldered to another board or connector, which is crucial for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications industries.
Applications in Advanced Circuit Designs
Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering finds extensive use in scenarios where space optimization and modularity are key. For instance, in IoT devices, these half holes enable the stacking of multiple PCBs, such as combining a sensor module with a processing unit, without the need for bulky connectors. This not only reduces the overall footprint but also enhances signal integrity by shortening the electrical paths between components. Similarly, in wireless communication systems like 5G routers or satellite modules, plated half holes facilitate edge connections that support high-frequency transmissions with minimal signal loss, thanks to the precise impedance control offered by the plating process.
Beyond consumer electronics, this technology is vital in medical devices, where reliability and miniaturization can be life-saving. Implantable devices or portable diagnostic tools often rely on half-hole PCBs to ensure secure interconnections in harsh environments. Additionally, industrial automation and robotics benefit from the robustness of plated half holes, which withstand vibrations and thermal cycling in manufacturing settings. By enabling designers to create more compact, efficient, and reliable systems, Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering plays a pivotal role in driving innovation across sectors, from smart homes to autonomous vehicles.
Quality Assurance and Precision Standards
Delivering precision and quality in Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering requires a rigorous quality assurance framework. Manufacturers adhere to international standards such as IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600, which define acceptability criteria for plated holes, including aspects like plating thickness, adhesion strength, and absence of voids. To achieve this, state-of-the-art facilities implement statistical process control (SPC) to monitor every stage of production, from drilling to final inspection. Environmental controls, such as cleanrooms and humidity regulation, further ensure that contaminants do not compromise the plating integrity.
Precision is also enhanced through advanced equipment, such as laser direct imaging (LDI) for accurate pattern transfer and automated plating lines that maintain consistent chemical baths. Regular testing, including microsectioning to examine cross-sections and thermal shock tests to assess durability under stress, validates that each batch meets the high demands of advanced circuit designs. By prioritizing these measures, manufacturers can guarantee that plated half holes not only perform electrically but also endure the mechanical stresses of assembly and operation, thereby reducing failure rates and enhancing product lifespan.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology advances, Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering continues to evolve, driven by trends like 5G, artificial intelligence, and flexible electronics. Future developments may include the integration of half holes with HDI (High-Density Interconnect) PCBs, allowing for even greater component density and faster data rates. Innovations in plating materials, such as using silver or palladium alloys, could improve conductivity and resistance to oxidation, catering to high-reliability applications in extreme environments. Additionally, the rise of sustainable manufacturing practices is prompting research into eco-friendly plating processes that reduce chemical waste while maintaining performance.
Another emerging trend is the combination of half holes with embedded components, where passive elements are buried within the PCB layers, further saving space. With the growth of the Internet of Things and edge computing, the demand for smaller, more powerful modules will only increase, positioning Professional Plating Half Holes PCB Engineering as a key technology for next-generation designs. By staying at the forefront of these innovations, engineers can continue to deliver precision and quality, enabling breakthroughs in electronics that shape our connected world.
REPORT