-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
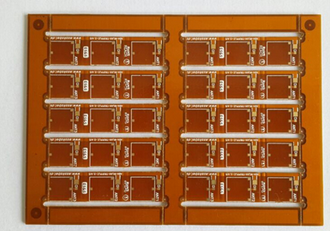
Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board Offering Optimal Electrical Connectivity And Mechanical Strength
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing, the demand for components that combine reliability, durability, and high performance has never been greater. Among the innovations addressing these needs, the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board stands out as a pivotal solution, offering optimal electrical connectivity and mechanical strength. This technology represents a significant leap forward from traditional rigid or standard flexible circuit boards, integrating specialized plating techniques along the edges to enhance both electrical and structural properties. As industries such as aerospace, medical devices, automotive systems, and consumer electronics push the boundaries of miniaturization and functionality, the limitations of conventional boards—such as susceptibility to wear, poor signal integrity, and mechanical failure—become increasingly apparent. The Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board emerges as a response to these challenges, designed to ensure seamless performance in demanding environments. By providing a robust interface for connections and reinforcing the board's edges, it not only improves electrical transmission but also extends the lifespan of electronic assemblies. This article delves into the intricacies of this advanced technology, exploring how it achieves superior connectivity and strength, and why it is becoming indispensable in modern electronic design.
Enhanced Electrical Connectivity Through Edge Plating
The core advantage of the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board lies in its ability to deliver optimal electrical connectivity, a critical factor in high-speed and high-frequency applications. Traditional flexible circuits often rely on soldered connections or connectors that can introduce resistance, signal loss, or electromagnetic interference. In contrast, edge plating involves depositing a conductive metal layer, typically copper followed by a protective finish like gold or nickel, along the board's perimeter. This creates a continuous, low-resistance path for electrical signals, reducing impedance and minimizing signal degradation. The result is improved signal integrity, which is essential for applications such as data transmission in telecommunications or precision sensing in medical equipment.
Moreover, the edge plating process enhances the board's reliability in dynamic or harsh conditions. For instance, in automotive electronics, where temperature fluctuations and vibrations are common, the plated edges maintain stable connections without the risk of dislodgment or corrosion. The plating also allows for direct insertion into connectors or sockets, eliminating the need for additional wiring and simplifying assembly. This not only streamlines manufacturing but also reduces potential points of failure, ensuring consistent performance over time. By optimizing electrical pathways, the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board supports higher data rates and more efficient power distribution, making it a preferred choice for advanced electronic systems.
Superior Mechanical Strength and Durability
Beyond electrical benefits, the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board excels in mechanical strength, addressing a common weakness in flexible circuits: vulnerability to physical stress. Flexible boards are often subjected to bending, twisting, or repeated flexing, which can lead to cracks, delamination, or connection failures. The edge plating technique reinforces the board's structure by adding a robust metal layer along the edges, effectively acting as a protective barrier. This reinforcement distributes mechanical loads more evenly, reducing the risk of damage during installation or operation. In applications like wearable technology or robotics, where boards must endure constant movement, this enhanced durability translates to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Additionally, the plating improves the board's resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. The metal coating seals the edges, preventing ingress of contaminants that could compromise electrical performance or cause short circuits. This is particularly valuable in industrial or outdoor settings, where electronics are exposed to harsh conditions. The combination of flexibility and strength allows the board to maintain its integrity even under extreme stress, ensuring reliable operation in mission-critical systems. By bolstering mechanical resilience, the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board enables designers to create more compact and robust devices without sacrificing performance.
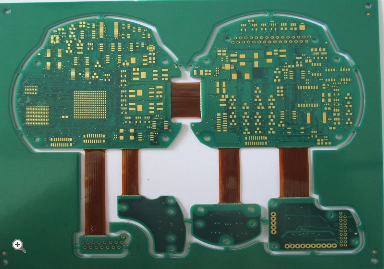
Design Flexibility and Integration Capabilities
The Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board offers unparalleled design flexibility, allowing engineers to innovate in space-constrained applications. Unlike rigid boards, flexible circuits can be bent or folded to fit into irregular shapes, and the edge plating enhances this adaptability by providing reliable connection points at the board's periphery. This facilitates seamless integration with other components, such as sensors, displays, or power sources, without the need for bulky connectors or cables. In consumer electronics, for example, this enables sleeker, lighter devices with improved functionality, from smartphones to wearable health monitors.
Furthermore, the technology supports high-density interconnects, enabling more circuits to be packed into a smaller area. The plated edges can serve as contact points for stacking multiple boards or connecting to external systems, streamlining complex assemblies. This is especially beneficial in aerospace and defense applications, where weight and space savings are paramount. The ability to customize the plating pattern and materials also allows for tailored solutions, meeting specific electrical or mechanical requirements. By enhancing integration capabilities, the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board empowers designers to push the boundaries of innovation while maintaining reliability.
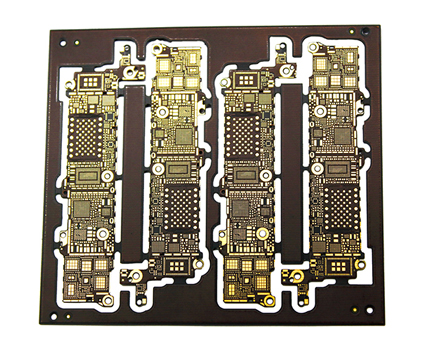
Applications Across Diverse Industries
The versatility of the Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Board makes it suitable for a wide range of industries, each benefiting from its unique properties. In the medical field, for instance, it is used in implantable devices and diagnostic equipment, where reliable electrical connections and biocompatibility are crucial. The edge plating ensures stable performance in sensitive environments, reducing the risk of device failure. Similarly, in automotive systems, the board supports advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicle components, where durability and signal integrity are essential for safety and efficiency.
In telecommunications and data centers, the board facilitates high-speed data transfer with minimal loss, supporting the growing demand for bandwidth. Its mechanical strength also makes it ideal for industrial automation, where equipment is subject to constant vibration and wear. As technology continues to advance, the adoption of Advanced Flexible Edge Plated Boards is expected to expand, driven by the need for more reliable and efficient electronic solutions. By offering a blend of optimal electrical connectivity and mechanical strength, this technology is poised to play a key role in shaping the future of electronics.
REPORT