-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
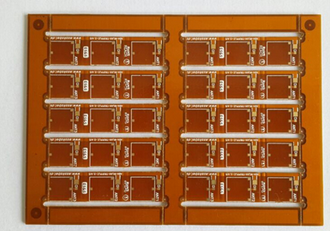
Reliable Flexible Edge Plated Circuit Board Supporting Complex Designs And Harsh Environments
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics, where devices are expected to perform flawlessly in increasingly compact, dynamic, and demanding conditions, the quest for a foundational component that marries durability with sophisticated functionality is paramount. Enter the reliable flexible edge plated circuit board—a technological marvel engineered specifically to support complex designs and thrive in harsh environments. This innovation represents a significant leap beyond traditional rigid PCBs and even standard flexible circuits. By integrating specialized edge plating—a process of depositing a conductive metal layer along the board's perimeter—with high-performance flexible substrates, this solution addresses critical challenges in modern electronics, from aerospace and automotive systems to advanced medical devices and wearable technology. Its unique construction not only ensures robust electrical connectivity and mechanical integrity but also unlocks new possibilities for three-dimensional packaging and resilient operation under stress, vibration, moisture, and extreme temperatures. As industries push the boundaries of what's possible, understanding the capabilities of this advanced circuit board becomes essential for engineers and designers aiming to build the next generation of reliable electronic systems.
Engineering Excellence: The Fusion of Flexibility and Robust Edge Plating
The core innovation of this circuit board lies in its hybrid architecture, which combines the inherent advantages of flexible printed circuits (FPCs) with the reinforced durability of edge plating. Flexible substrates, typically made from polyimide or similar materials, provide excellent bendability, lightweight properties, and resistance to thermal expansion. This allows the board to conform to unconventional shapes and fit into tight spaces, enabling complex, multi-layer designs that would be impossible with rigid boards.
However, flexibility alone is insufficient for harsh environments where repeated flexing, mechanical shocks, or connector insertion cycles can compromise reliability. This is where edge plating proves transformative. The process involves metallizing the board's edges, creating a continuous conductive surface that wraps around from the top to the bottom layers. This edge plating serves multiple critical functions: it shields the internal circuitry from environmental contaminants like dust and humidity, provides enhanced grounding and shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI), and most importantly, reinforces the plated through-holes (PTHs) and connection points along the board's periphery.
By fortifying these vulnerable edge areas, the board achieves exceptional mechanical strength. The plated edge acts as a structural brace, preventing delamination, crack propagation in the dielectric layers, and wear on contact pads during mating and unmating cycles with connectors. This synergy between a flexible body and a hardened edge creates a circuit board that is both adaptable and extraordinarily durable, forming the foundation for reliability in demanding applications.
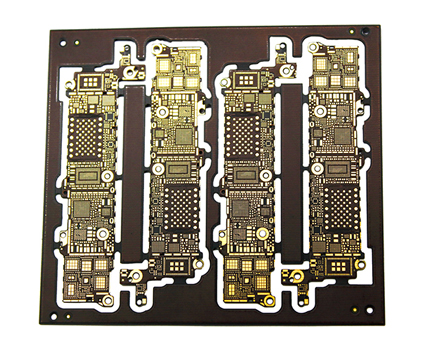
Enabling Complex and High-Density Design Architectures
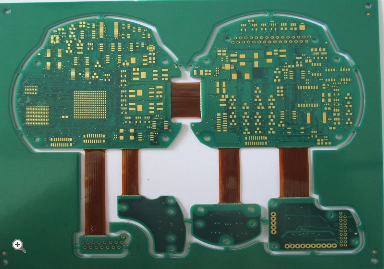
One of the most compelling advantages of reliable flexible edge plated boards is their capacity to support highly complex and dense electronic designs. Traditional rigid boards are limited to two-dimensional layouts, often requiring bulky wire harnesses and connectors to link multiple boards in a system. This increases weight, potential failure points, and assembly complexity. In contrast, flexible edge plated boards can be designed to fold, twist, or flex into three-dimensional configurations, consolidating what would be several interconnected rigid boards into a single, unified assembly.
The edge plating technology is pivotal in this context. It enables robust interconnections between different flexible sections or between the flexible board and rigid components. Designers can route high-speed signals or power lines to the board's edge with confidence, knowing the edge plating provides a low-resistance, stable pathway. This facilitates innovative packaging solutions, such as "flex-to-install" designs where the board snakes through cramped device housings, or "rigid-flex" designs where flexible segments with plated edges seamlessly integrate with rigid board sections for mounting chips and connectors.
Furthermore, the enhanced reliability of the edge connections allows for higher component density. Designers can place components and routing closer to the board's edges without fear of connection failure, maximizing the use of available space. This is crucial for modern devices like miniaturized sensors, implantable medical equipment, or compact avionics, where every cubic millimeter counts and performance cannot be sacrificed for size.
Unmatched Performance in Harsh and Extreme Environments
The true test of any electronic component is its performance under duress, and this is where reliable flexible edge plated circuit boards truly excel. They are specifically engineered to withstand conditions that would cripple standard electronics. The combination of material science and advanced plating creates a barrier against multiple environmental stressors.
Firstly, the edge plating forms a hermetic seal along the board's perimeter, significantly improving resistance to moisture ingress, corrosive gases, and ionic contaminants. This is vital for applications in automotive under-the-hood systems, offshore oil and gas equipment, or outdoor telecommunications infrastructure, where condensation and corrosive elements are constant threats. The polyimide base material itself offers excellent chemical resistance and stable performance across a wide temperature range, often from -55°C to over 200°C.
Secondly, the mechanical resilience afforded by the edge plating is critical for environments subject to vibration, shock, and constant motion. In aerospace applications, for instance, circuit boards must endure the intense vibrations of launch and flight. The reinforced edges prevent solder joint fatigue and interconnection failures. Similarly, in industrial robotics or military field equipment, where drops and impacts are possible, the board's ability to absorb and dissipate mechanical stress without internal damage ensures continuous operation.
Finally, the edge plating enhances thermal management. The conductive metal edge can help dissipate heat away from sensitive components, and the overall robust construction prevents performance degradation from thermal cycling. This holistic approach to environmental protection—encompassing mechanical, climatic, and chemical challenges—makes these boards indispensable for mission-critical systems where failure is not an option.
Driving Innovation Across Critical Industries
The unique properties of reliable flexible edge plated circuit boards have catalyzed advancements across a diverse spectrum of industries. In each field, they solve specific, high-stakes problems, enabling new products and improving the reliability of existing ones.
In the aerospace and defense sector, these boards are used in satellite systems, avionics controls, and missile guidance systems. Their light weight reduces payload, their flexibility allows for installation in curved airframes, and their harsh-environment durability ensures functionality in the vacuum of space or the extreme conditions of high-altitude flight. The edge plating is particularly valued for maintaining signal integrity in high-frequency radar and communication systems by providing superior EMI shielding.
The automotive industry, especially with the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles, relies on them for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), battery management systems (BMS), and in-cabin electronics. Located in engine compartments or within moving parts like steering columns, these boards withstand temperature swings, fluid exposure, and constant vibration over the vehicle's lifespan. The robust edge connections are essential for the dense network of sensors and controllers that modern vehicles depend on.
Medical technology represents another frontier. From portable diagnostic devices to implantable neurostimulators, these boards offer the biocompatibility, miniaturization, and absolute reliability required. They can be designed to fit within the contours of the human body or inside handheld medical tools that undergo frequent sterilization. The edge plating ensures that connections remain secure over years of service, a non-negotiable requirement for life-sustaining equipment.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands into industrial and agricultural settings, these circuit boards provide the rugged backbone for sensors monitoring pipelines, factory floors, or environmental conditions. Their ability to support complex, miniaturized designs while enduring harsh outdoor or industrial environments makes them a key enabler of the connected world. In essence, wherever technology faces physical and environmental challenges, the reliable flexible edge plated circuit board emerges as a foundational solution, empowering engineers to design with greater ambition and confidence.
REPORT