-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
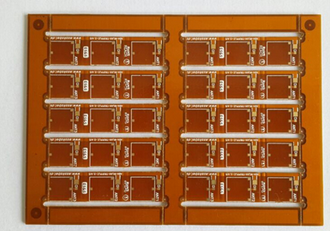
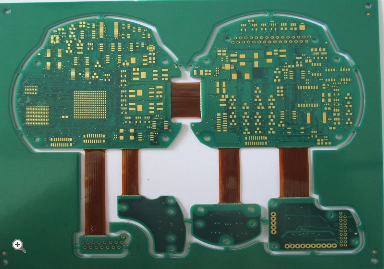
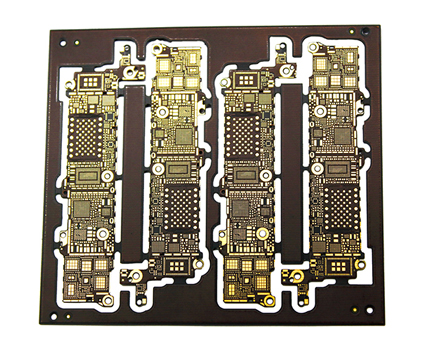
State Of The Art Flexible Edge Plating Board Delivering Precision And Durability In Modern Electronics
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern electronics, where devices are becoming increasingly compact, powerful, and integrated into every facet of daily life, the demand for advanced printed circuit board (PCB) technology has never been greater. Among the critical innovations driving this progress is the State of the Art Flexible Edge Plating Board, a sophisticated solution engineered to deliver unparalleled precision and durability. This technology represents a significant leap forward from traditional rigid PCBs, enabling the creation of more resilient, space-efficient, and high-performance electronic systems. As industries from consumer electronics and automotive to medical devices and aerospace push the boundaries of what is possible, the need for reliable interconnections and robust board structures becomes paramount. Flexible edge plating, a specialized process that involves depositing a conductive metal layer along the board's edges, addresses these challenges by enhancing electrical connectivity, mechanical strength, and environmental resistance. This article delves into the intricacies of this cutting-edge technology, exploring how it is revolutionizing modern electronics by ensuring that devices not only meet but exceed the rigorous demands of today's applications.
Enhanced Electrical Performance and Signal Integrity
The primary function of any PCB is to facilitate reliable electrical connections between components, and flexible edge plating excels in this regard by optimizing signal integrity across the board. By applying a continuous conductive layer along the edges, this technology reduces impedance discontinuities and minimizes signal loss, which is crucial for high-frequency applications such as 5G communications, advanced computing, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The precision in the plating process ensures uniform thickness and coverage, preventing issues like signal reflection or crosstalk that can degrade performance in complex circuits.
Moreover, flexible edge plating enhances the board's ability to handle higher current densities, supporting the power requirements of modern electronics without compromising safety or efficiency. This is particularly important in applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, where stable power delivery is essential. The improved conductivity also contributes to better thermal management, as the plated edges can help dissipate heat more effectively, reducing the risk of overheating and extending the lifespan of electronic components. In essence, this aspect of the technology ensures that devices operate smoothly under demanding conditions, maintaining optimal functionality over time.
Superior Mechanical Durability and Flexibility
One of the standout features of flexible edge plating is its ability to combine durability with flexibility, making it ideal for applications where boards are subject to bending, twisting, or vibration. Traditional rigid PCBs can crack or fail under mechanical stress, but flexible boards with edge plating are designed to withstand such challenges. The plated edges reinforce the board structure, adding strength to the connection points and reducing the likelihood of delamination or breakage during assembly or use.
This mechanical robustness is especially valuable in dynamic environments, such as wearable technology, foldable smartphones, and automotive electronics, where boards must endure constant movement and environmental exposure. The flexibility allows for more creative and space-saving designs, enabling engineers to fit advanced electronics into smaller, irregularly shaped enclosures. Additionally, the plating process can be tailored to specific materials, such as polyimide or polyester substrates, further enhancing the board's resilience against factors like moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. As a result, devices incorporating this technology benefit from longer operational lifespans and reduced maintenance needs, translating to cost savings and improved user satisfaction.
Advanced Manufacturing Precision and Quality Control
The production of state-of-the-art flexible edge plating boards involves sophisticated manufacturing techniques that prioritize precision at every stage. From the initial design phase to the final inspection, advanced processes like laser drilling, automated plating, and high-resolution imaging are employed to ensure that each board meets exacting standards. This level of precision is critical for applications where even minor defects can lead to system failures, such as in medical implants or aerospace instrumentation.
Quality control measures, including rigorous testing for conductivity, adhesion, and environmental resistance, guarantee that the plated edges perform reliably under real-world conditions. Manufacturers often use techniques like X-ray fluorescence and cross-sectional analysis to verify the uniformity and integrity of the plating, minimizing the risk of voids or inconsistencies. By leveraging these advanced methods, the technology supports the trend toward miniaturization and higher component density in electronics, allowing for more complex circuits without sacrificing reliability. This focus on precision not only enhances product performance but also fosters innovation, as designers can push the limits of what is achievable with confidence in the underlying board technology.
Environmental Sustainability and Industry Applications
In today's world, sustainability is a key consideration in electronics manufacturing, and flexible edge plating contributes to this goal by enabling more efficient and durable products. The enhanced durability of these boards means that devices last longer, reducing electronic waste and the need for frequent replacements. Furthermore, the materials and processes used in edge plating can be optimized to minimize environmental impact, such as by employing lead-free or recyclable metals and reducing energy consumption during production.
The versatility of this technology has led to its adoption across a wide range of industries, each benefiting from its unique advantages. In the medical field, for example, flexible edge plating boards are used in diagnostic equipment and implantable devices, where reliability and biocompatibility are paramount. In automotive applications, they support advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicle powertrains, ensuring safety and performance under harsh conditions. Consumer electronics, from smartphones to smart home devices, also rely on these boards to deliver sleek, durable designs that meet consumer expectations. As industries continue to innovate, the role of flexible edge plating in enabling next-generation electronics will only grow, underscoring its importance in shaping a more connected and sustainable future.
REPORT